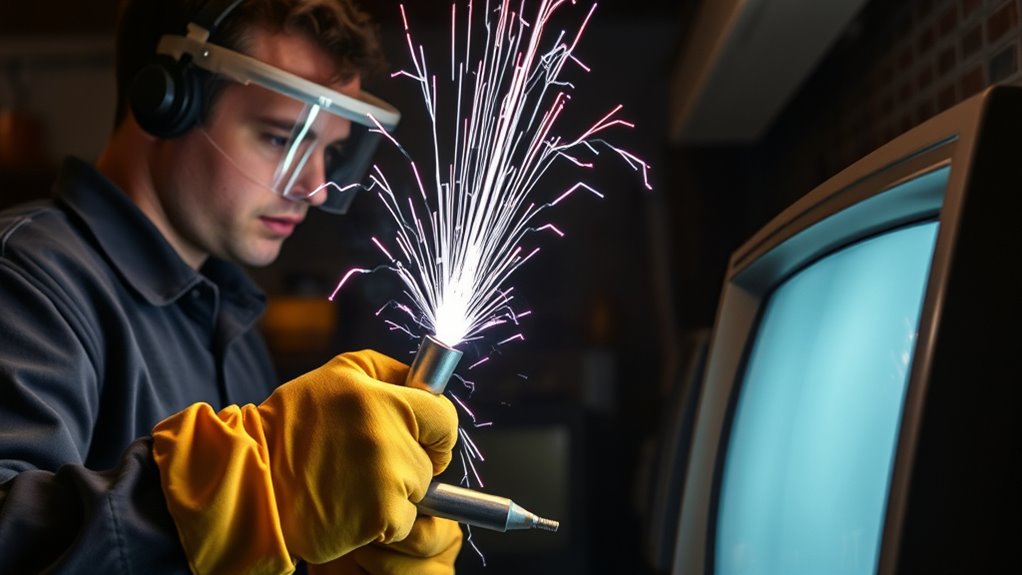
When working with high-voltage CRTs, always wear proper safety gear like insulated gloves, eye protection, and grounded tools. Before discharging, unplug the device, locate discharge points, and connect a resistor across the anode cap to safely release stored energy. Use a multimeter to verify no residual voltage remains before handling components. Keep your workspace dry, organized, and free of metal jewelry. Following these safety tips guarantees you avoid shocks and injuries—learn more to stay fully protected.
Key Takeaways
- Always wear insulated gloves and eye protection before discharging a CRT to prevent electrical shocks.
- Use a properly rated resistor (e.g., 10kΩ, 5W) across the anode cap to safely discharge residual high voltage.
- Verify complete discharge with a multimeter set to high-voltage range before handling components.
- Ensure the CRT is unplugged and properly grounded to eliminate stored energy risks.
- Keep emergency supplies and first aid kits nearby, and follow safety protocols during all procedures.
Understanding the Risks of High-Voltage CRTs
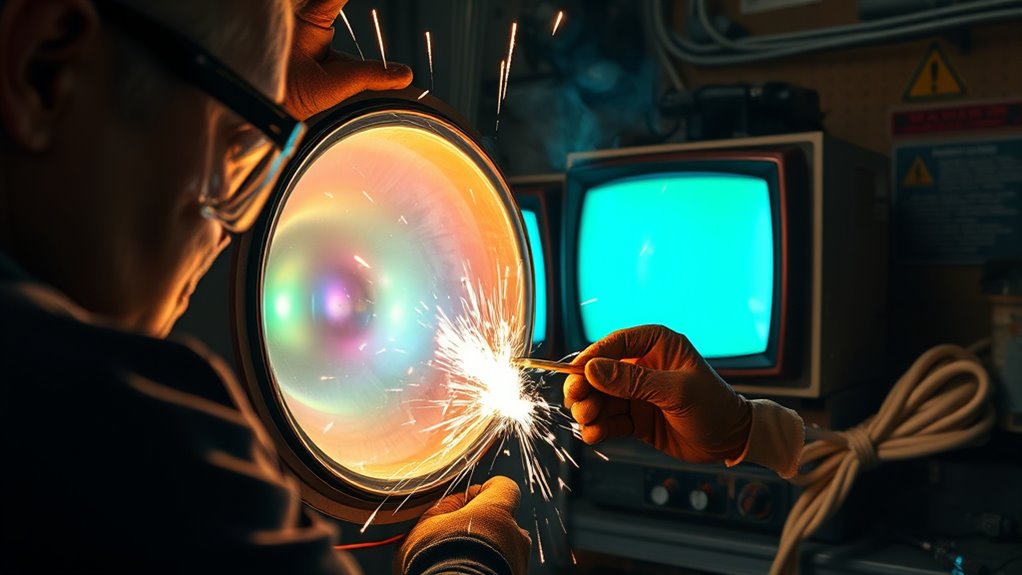

High-voltage CRTs can pose serious dangers if not handled properly. You need to understand the voltage hazards involved, as these can cause severe shocks. The high voltages stored within CRTs create discharge risks that may happen unexpectedly, even after powering down the device. When working around these components, you might not see or feel the stored energy, making it *essential* to treat every CRT as potentially dangerous. Ignoring these risks can lead to electrical shocks, burns, or even more severe injuries. Always recognize that the high voltage isn’t just a minor concern; it’s a *vital* safety issue. Being aware of the potential dangers helps you stay alert and cautious during any repair or maintenance task involving high-voltage CRTs. Additionally, understanding the role of contrast ratio can help you better assess the safety and performance of your CRT setup.
Gathering Proper Safety Equipment

Before working on a CRT, you need to gather the right safety equipment. Wearing protective gear like gloves and eye protection is essential, and using insulated tools keeps you safe from accidental shocks. Ensuring you have these essentials ready can make a critical difference during discharge procedures. Additionally, understanding electrical safety principles can help you better prepare for potential hazards.
Protective Gear Essentials
Equipping yourself with the right protective gear is vital for safely discharging high-voltage CRTs. Start with electrical insulation gear, such as rubber gloves and mats, to prevent accidental shocks. Make sure your safety training covers proper handling techniques and safety protocols, so you’re aware of potential hazards. Wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from any unexpected sparks or debris. A grounded wrist strap can help dissipate static buildup, reducing the risk of unintended discharge. Remember, high-voltage environments demand strict adherence to safety standards. Proper protective gear acts as your first line of defense, minimizing risks and helping you focus on the task safely. Always verify your equipment’s integrity before beginning, as proper maintenance ensures maximum protection. Never skip this essential step before proceeding with CRT discharge procedures.
Insulated Tools Importance
Using insulated tools is essential when working with CRTs because they provide an added layer of safety against accidental electrical contact. Insulated tools are specifically designed with non-conductive handles and proper tool insulation, preventing electrical shocks if you inadvertently touch live components. Always choose tools approved for electrical work, guaranteeing their insulation remains intact and effective. Relying on well-insulated tools minimizes the risk of short circuits or sparks that could cause injury or damage. Keep in mind, even the best tool insulation isn’t foolproof—inspect tools before use for cracks or wear. Using the right insulated tools ensures you maintain a safer working environment, reducing potential hazards during high-voltage CRT discharges. Proper safety starts with the right equipment, so never compromise on tool insulation. Additionally, understanding the self-watering plant pots system can help you maintain optimal moisture levels without frequent intervention, which is crucial when working with high-voltage equipment where minimizing distractions is important.
Preparing Your Workspace for Safe Discharging
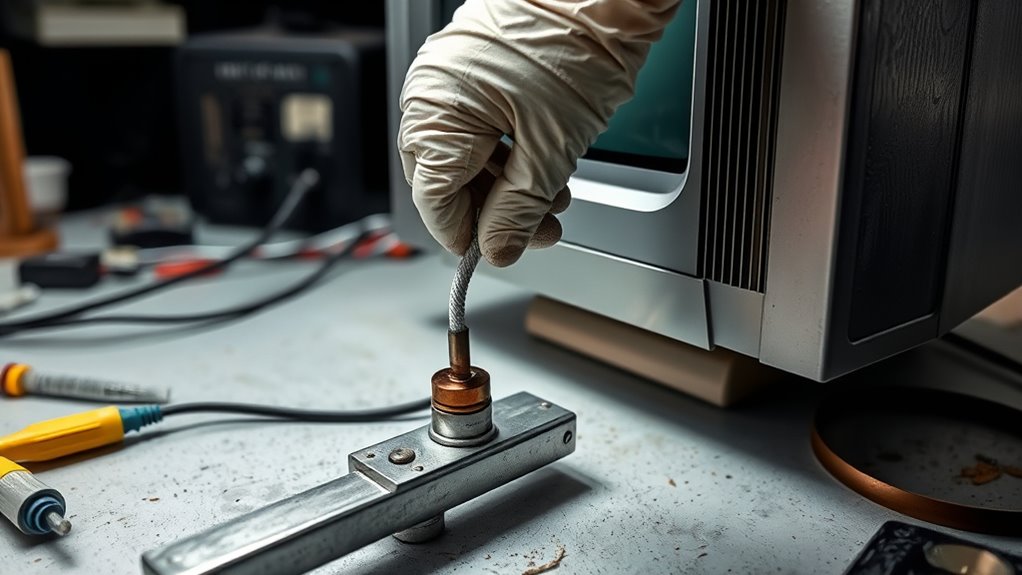

To guarantee safety during CRT discharge, you need to prepare your workspace carefully. First, organize your workspace to keep tools, cables, and safety equipment within easy reach. Clear the area of unnecessary items to prevent accidents and distractions. Ensure your workspace is well-lit and ventilated. Have emergency preparedness supplies nearby, such as insulated gloves, a fire extinguisher, and a first aid kit. Keep a clear path to an exit in case you need to leave quickly. Remove any metal jewelry or conductive objects that could cause shorts or shocks. Mark the workspace with warning signs if others are nearby. Proper organization and readiness help minimize risks, ensuring you can focus on discharging the CRT safely and effectively. Additionally, understanding high-voltage safety protocols is crucial to prevent accidents and injuries during the process.
Identifying and Locating the CRT’s Discharge Point
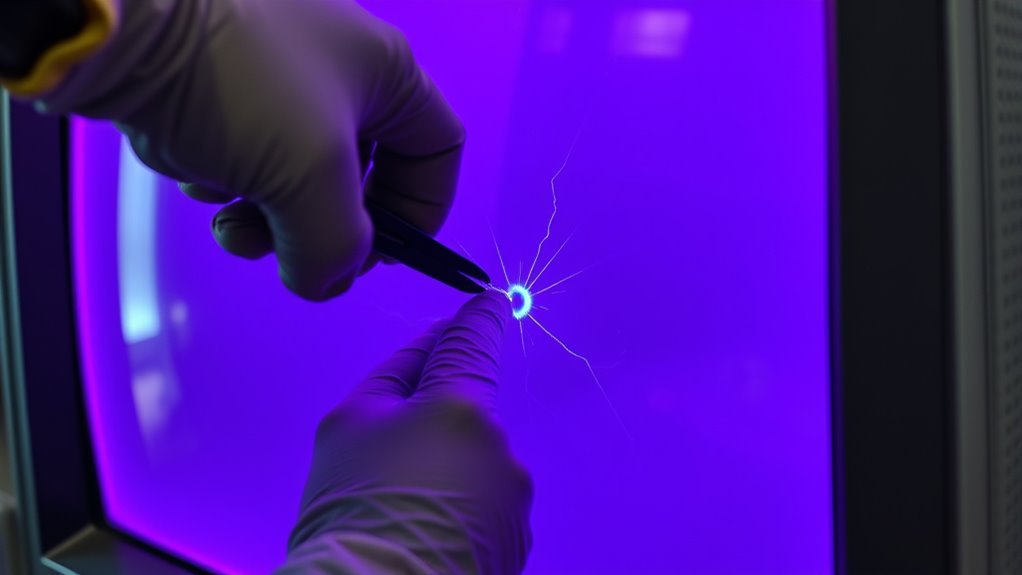
To safely discharge a CRT, you need to identify its discharge point accurately. Use visual inspection techniques to spot common discharge locations, such as the anode cap or the metal chassis. Knowing these points helps you discharge the high voltage safely and effectively. Additionally, ensuring the discharge process is performed with proper tools and precautions minimizes the risk of electric shock.
Visual Inspection Techniques
Before attempting to discharge a high-voltage CRT, you need to visually identify where the discharge point is located. Start by inspecting the CRT’s internal components for signs of damage or corrosion, which can indicate potential discharge areas. Carefully remove the CRT’s cover in a well-lit environment, and look for any discoloration, cracks, or burnt spots on the anode cap or nearby components. Conduct an external damage assessment, checking for broken wires or melted insulation that could reveal discharge paths. Remember, the discharge point is often near the high-voltage terminal, so pinpoint any irregularities in that vicinity. A thorough visual inspection helps assure you target the correct area, reducing the risk of accidental shocks during discharging. Additionally, understanding the electrical hazards involved can enhance your safety precautions during the process.
Common Discharge Locations
High-voltage discharge points on a CRT are typically located near the anode cap, where the high-voltage wire connects to the tube. To locate the discharge point, look for areas where residual charge may linger, especially around the anode cap, the metal chassis, and the neck of the tube. Always prioritize capacitor safety and grounding techniques to prevent electric shock. Understanding industry transformations can help you stay informed about the latest safety protocols and equipment updates. Key discharge locations include: – Anode cap connection – Metal chassis around the CRT – Neck of the tube. Understanding these areas helps you safely discharge stored energy. Using proper grounding techniques ensures you’re grounded before touching any discharge point. Always verify the voltage with a meter before proceeding, and discharge at the identified points to minimize risk.
Step-by-Step Discharging Procedure

Discharging a CRT safely requires following a precise, step-by-step process to guarantee your safety. First, ensure you’re wearing insulated gloves and eye protection, adhering to safety regulations. Use a high-voltage probe or a resistor (typically 10kΩ, 5W) to discharge the anode. Follow these steps:
| Step | Action | Tool/Component |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power off and unplug set | N/A |
| 2 | Attach resistor across the anode | 10kΩ resistor |
| 3 | Hold resistor leads securely | Insulated pliers |
| 4 | Wait for discharge completion | Observe voltage indicator |
| 5 | Remove resistor and verify | Multimeter |
This process minimizes electrical jargon confusion while ensuring safety regulations are met.
Verifying the Complete Discharge

After completing the discharging process, it’s important to verify that no residual voltage remains. You can do this by checking the charge indicators or using a multimeter to perform discharge verification. This step guarantees the CRT is safe to work on and prevents electric shock. Ensuring proper data privacy measures are in place during testing is also crucial to protect sensitive information. To confirm complete discharge, consider these points:
- Test the anode cap with a properly rated probe for any lingering charge.
- Use a multimeter set to high-voltage range to check for voltage presence.
- Look for consistent zero or near-zero readings to validate that no residual voltage exists.
Always double-check with your tools before proceeding. Proper discharge verification is vital for safety and to avoid unexpected shocks when handling high-voltage components.
Additional Safety Precautions and Tips

To guarantee your safety while working with CRTs, always wear insulated gloves and use tools with proper insulation. Proper grounding techniques are essential; verify the CRT is grounded to prevent accidental shocks. Use a grounding strap to discharge residual voltage safely. Keep an emergency response plan ready, including a first aid kit and quick access to emergency services. In case of accidental shock, disconnect power immediately and seek medical attention. Always work in a dry, well-ventilated area to reduce electrical hazards. Being aware of trust issues with boyfriend no-shows can help you stay alert to potential relationship problems that might cause distraction or stress during safety procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Signs of Residual Charge After Discharging?
After discharging a high-voltage CRT, you should check for residual charge indicators. If you see any sparks, hear crackling sounds, or notice a tingling sensation when touching the device, these are signs of residual charge. To guarantee safety, always perform discharge verification by using a suitable meter or screwdriver. If residual charge remains, repeat the discharge process until you get a clear confirmation that no stored energy is present.
How Often Should CRT Discharges Be Repeated for Safety?
Think of CRT discharge as watering a garden—you need to do it just enough to keep it safe. You should discharge the CRT once, then wait at least 15 minutes before repeating to make sure residual charge dissipates. Follow recommended safety intervals, usually around 15-30 minutes, especially if you notice any residual charge signs. Always double-check with a tester before handling, and don’t rush the process—safety’s worth the patience.
Can Improper Discharging Damage the CRT or Other Components?
Improper discharging can definitely damage your CRT or other components. If you don’t follow proper procedures, high-voltage energy might cause internal damage or weaken the tube over time. To guarantee equipment safety, always use the correct tools and techniques when discharging. Neglecting proper procedures risks not only damaging the CRT but also creating safety hazards for you. Proper discharging methods are essential for preserving your equipment and preventing accidents.
Are There Specific Gloves That Provide Better Protection During Discharging?
You should choose gloves made from rubber or latex, as these materials offer excellent insulation. Look for gloves with high insulation ratings to guarantee maximum protection during discharging. Thicker gloves provide better resistance against high voltage shocks, but make sure they still allow for dexterity. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications to confirm the gloves meet safety standards for high-voltage work, and replace them if they show signs of wear or damage.
What Are the Legal Considerations for Working on High-Voltage CRTS?
When working on high-voltage CRTs, you must ensure legal compliance by following all relevant safety regulations and industry standards. It’s vital to obtain liability waivers from anyone involved to protect yourself legally. You should also document safety procedures and training, as these can be critical if legal issues arise. Always stay updated on local laws and guidelines, and consult with professionals or legal advisors to minimize your legal risks.
Conclusion
By following these safety tips, you’ll turn a potentially catastrophic shock into a manageable task. Remember, a high-voltage CRT can deliver a jolt powerful enough to knock you off your feet—so don’t take chances. Stay vigilant, double-check your work, and prioritize safety at every step. With proper precautions, you’ll discharge your CRT confidently, avoiding disaster and ensuring your workspace remains safe. Your safety is worth more than a thousand sparks—trust me, it’s a game-changer.









